The Python ord() function is used to return an integer of the given single Unicode character. The returned integer represents the Unicode code point.
Inversely, the Python chr() function takes a Unicode code point (integer) and returns a string.
Tip: The Unicode code point is given the meaning by Unicode standard, which is a number.
See the section below for learning how to use the ord() and chr() functions with examples.
An example of using Python ord() function
In this simple example, the code point of the letter ‘B’ is returned by using the ord() function.
# An example of ord() function
print("The Unicode code point for B = " ,ord('B'))
Output:
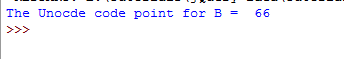
The code points of numbers 0-9 by using range example
In the following example, a range of 10 numbers (0-9) is created. A for loop is used to iterate through the range. The ord Python function is used to display the code point of each number in the range.
#Know Unicode code points of numbers by ord() function
for x in range(10):
print ("The Unicode code point of",x ,'=' ,ord(str(x)))
Output:

As range items are numbers, so it will produce an error if directly used in the ord() function. As such, ord() takes a string, so str() function is used for converting the number into the string.
A user entered character example
For this example, the character is taken by the user by using the input function. Enter a single character and ord() function will return the Unicode code point of that character. Have a look:
str_ord = input("Enter a character?")
cde_pt = ord(str_ord)
print("The Unicode code point of the character",str_ord ,"=" ,cde_pt)
Output:

The chr() function example
The chr(i) method is the inverse of ord() function; it takes Unicode code point (which is an integer number) and returns a string.
In this example, different codes are given in the chr() function and its returned values are displayed:
#A demo of using chr() function
print("Unicode code point 65 = ", chr(65))
print("Unicode code point 36 = ", chr(36))
print("Unicode code point 36 = ", chr(163))
print("Unicode code point 36 = ", chr(38))
print("Unicode code point 1114112 = ", chr(1114112))
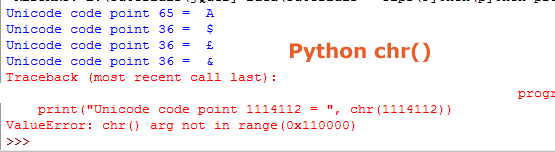
The chr() function has certain range which is 0 through 1,114,111 (0x10FFFF in base 16). If you enter a value which is out of the range, an error (ValueError) occurs as shown in the last part of this example.
An example of using range with chr()
For the final example, this is the inverse of the example that we used with Python range and ord() function. This time, a range is created between 65 – 80 numbers that are used as the argument in the chr() function as follows:
for x in range(65,80,1):
print ("code point",x ,'=' ,chr(x))
Result:
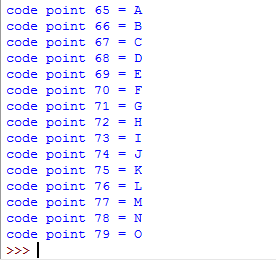
You can see, the characters from A-O are displayed.
