How to append DataFrame in Pandas
In order to append a DataFrame, Pandas has DataFrame.append method.
However, the append method is deprecated since 1.4.0 version.
Instead of the append method, you should use Pandas.concat method to add/append data in the data frames.
In this tutorial, we will show you examples of using the concat() method for joining two or more data frames in Python programs.
Syntax of concat()
Following is the complete syntax of concat() method in Pandas:
pandas.concat(objs, *, axis=0, join=’outer’, ignore_index=False, keys=None, levels=None, names=None, verify_integrity=False, sort=False, copy=True)
Let us use concat() method with a few of its parameters below.
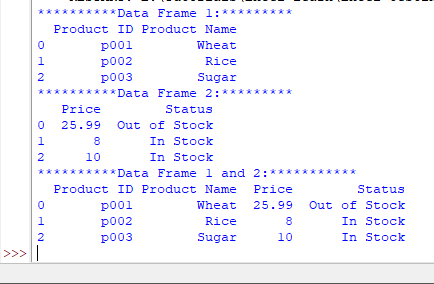
An example of concatenating two data frames
In this example, we have created a data frame based on the Python list.
This data frame is displayed on the screen.
This is followed by creating another Data Frame based on list 2. This data frame is also displayed on the screen.
Then we appended that to the first DF by concat() method and displayed concatenated DFs.
Python program:
import pandas as pd
#First Data Frame's data
product_list1 = [ ['p001', "Wheat"],
['p002', "Rice"],
['p003', "Sugar"]
]
#Second Data Frame's data
product_list2 = [ ["25.99","Out of Stock"],
["8","In Stock"],
["10","In Stock"]
]
#Creating First data frame
df_1 = pd.DataFrame (product_list1, columns = ['Product ID', 'Product Name'])
print("**********Data Frame 1:*********")
print(df_1)
#Second Data frame based on product_list2
df_2 = pd.DataFrame (product_list2, columns = ['Price', 'Status'])
print("**********Data Frame 2:*********")
print(df_2)
#Concatenating both Data Frames
print("**********Data Frame 1 and 2:***********")
print(pd.concat([df_1, df_2], axis=1))
Output:
An example of using concat() method with Dict
In the above example, you have seen the columns are added ahead after we concatenated the first DF to the second DF.
In the example below, we will create two dictionaries in Python.
The first dictionary contains Column names and three records of the telephone directory (Name and Phone No). On that bases, we created a DataFrame object.
This data frame is displayed on the screen.
This is followed by creating another dictionary which is used for creating a second Data Frame. There we created a row to be appended at the end of the first DF.
For clarity, data frames before and after concatenation are displayed:
Python program:
import pandas as pd
#Creating first dictionary with columns and three rows
tel_dir1 = {'Name': ['Mike','Haynes','Mina'],
'Phone No':[123445689,45678910, 635363636]}
#Second dictionary with columns and a row
tel_dir2 = {'Name': ['Raina'],
'Phone No':[458745141]}
df_1 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(tel_dir1)
print("**********Data Frame 1:***********")
print(df_1)
#Create data frame based on second dict
df_2 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(tel_dir2)
#Display data frame 2
print("**********Data Frame 2:***********")
print(df_2)
#Concatenating both Data Frames
print("**********Data Frame 1 and 2 after appending:***********")
print(pd.concat([df_1, df_2], axis=0))
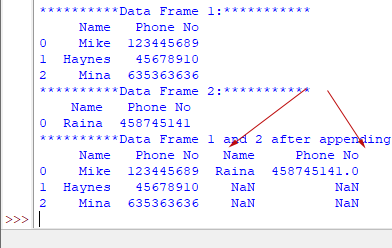
Result:
**********Data Frame 1:*********** Name Phone No 0 Mike 123445689 1 Haynes 45678910 2 Mina 635363636 **********Data Frame 2:*********** Name Phone No 0 Raina 458745141 **********Data Frame 1 and 2 after appending:*********** Name Phone No 0 Mike 123445689 1 Haynes 45678910 2 Mina 635363636 0 Raina 458745141
Notice the axis parameter in the concat method. This time we used axis=0.
As a result, the second data frame is appended at the end of the first DF, and though the second DF also contained column names, the concatenated result does not include this.
So, if we have used axis = 1, as in the first example the result:
An example of concatenating two data frames and using keys parameter
You may also use the keys parameter of the concat() method for constructing the hierarchical index.
In that case, the passed keys are used at the outermost level.
See the example below where we created three data frames and concatenated along with keys:
import pandas as pd
# creating three DFs
df_1 = pd.DataFrame({'Col1': ['X', 'Y', 'Z'],
'Col2': ['X', 'Y', 'Z']})
#Display data frame 1
print("**********Data Frame 1:*********")
print(df_1)
df_2 = pd.DataFrame({'Col1': ['A', 'B', 'C'],
'Col2': ['A', 'B', 'C']})
#Display data frame 2
print("**********Data Frame 2:*********")
print(df_2)
df_3 = pd.DataFrame({'Col1': ['I', 'J', 'K'],
'Col2': ['I', 'J', 'K']})
#Display data frame 3
print("**********Data Frame 3:*********")
print(df_3)
# Concatenating three DFs with keys
print('**********After concatenating:**********')
print(pd.concat([df_1, df_2, df_3],
keys = ['DF_1', 'DF_2','DF_3']))
Output:

