How to Sort Data Frames in Pandas
Pandas data frame has a sort_values method that is used to sort the data frame’s data in ascending or descending order.
The sorting can be based on column labels.
The sort_values method has different parameters as shown in the syntax below.
Syntax
DataFrame.sort_values(by, *, axis=0, ascending=True, inplace=False, kind=’quicksort’, na_position=’last’, ignore_index=False, key=None)
Let us show you examples of using sort_values with its parameters below.
An example of sorting results by a column label in ascending order
In the Python program below, we created a data frame with three columns and five rows of data.
Then we displayed the data frame in its original form.
This is followed by using the sort_values method where we only specified the column label to sort the results.
Python program:
import pandas as pd
#A list to be used for Data Frame
emp_data = [ ['Emp1', "Mike", 5600],
['Emp2', "Michelle", 4750],
['Emp3', "Ben", 6500],
['Emp4', "Shabee", 3600],
['Emp5', "Mina", 3250]
]
#Creating data frame
df_emp = pd.DataFrame (emp_data, columns = ['ID', 'Name', 'Salary'])
#Display data frame before sorting
print("DF in Orginal Order")
print(df_emp)
#Display data frame after sorting
print("===================")
print("DF After Sorting")
print(df_emp.sort_values(by='Name'))
Output:
DF in Orginal Order ID Name Salary 0 Emp1 Mike 5600 1 Emp2 Michelle 4750 2 Emp3 Ben 6500 3 Emp4 Shabee 3600 4 Emp5 Mina 3250 =================== DF After Sorting ID Name Salary 2 Emp3 Ben 6500 1 Emp2 Michelle 4750 0 Emp1 Mike 5600 4 Emp5 Mina 3250 3 Emp4 Shabee 3600
You can see, the results are sorted by Employee names in the data frame.
Sorting data frame in descending order
As it can be seen in the syntax, the default value for sorting order is ascending i.e.
ascending=True
By using the False value, you may get the data sorted in descending order.
See the example below where we used the same data frame and sorted results in descending order.
Program:
import pandas as pd
#A list to be used for Data Frame
emp_data = [ ['Emp1', "Mike", 5600],
['Emp2', "Michelle", 4750],
['Emp3', "Ben", 6500],
['Emp4', "Shabee", 3600],
['Emp5', "Mina", 3250]
]
#Creating data frame
df_emp = pd.DataFrame (emp_data, columns = ['ID', 'Name', 'Salary'])
#Display data frame before sorting
print("DF in Orginal Order")
print(df_emp)
#Display data frame after ascending=False
print("===================")
print("DF After Sorting in Descending Order")
print(df_emp.sort_values(by='Name', ascending=False))
Output:
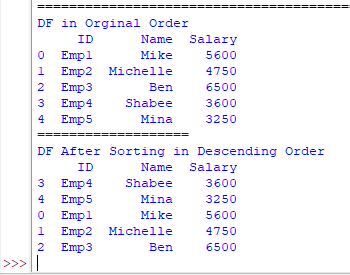
The example of sorting by salary column
The example below sorts the result in descending order based on the salary column:
import pandas as pd #A list to be used for Data Frame emp_data = [ ['Emp1', "Mike", 5600], ['Emp2', "Michelle", 4750], ['Emp3', "Ben", 6500], ['Emp4', "Shabee", 3600], ['Emp5', "Mina", 3250] ] #Creating data frame df_emp = pd.DataFrame (emp_data, columns = ['ID', 'Name', 'Salary']) #Sort results by Highest to loweset salary print(df_emp.sort_values(by='Salary', ascending=False))
Result:
ID Name Salary 2 Emp3 Ben 6500 0 Emp1 Mike 5600 1 Emp2 Michelle 4750 3 Emp4 Shabee 3600 4 Emp5 Mina 3250
Sort result by two columns example
You may also sort the results by providing two or more columns.
The example below sorts the results by name and salary columns in our example data frame:
import pandas as pd #A list to be used for Data Frame emp_data = [ ['Emp1', "Mike", 5600], ['Emp2', "Michelle", 4750], ['Emp3', "Ben", 6500], ['Emp4', "Shabee", 3600], ['Emp5', "Mina", 3250] ] #Creating data frame df_emp = pd.DataFrame (emp_data, columns = ['ID', 'Name', 'Salary']) #Sort results by multiple columns print(df_emp.sort_values(by=['Name', 'Salary'], ascending=False))
Output:
ID Name Salary 3 Emp4 Shabee 3600 4 Emp5 Mina 3250 0 Emp1 Mike 5600 1 Emp2 Michelle 4750 2 Emp3 Ben 6500
Using ignore_index parameter example
By default, the ignore_index= False. That means the index column numbers remain in place after sorting the results. In the above example output, you can see 3, 4, 0, 1, 2, and the numbers that are for the original DF.
If you may ignore_index=True then the resulting axis after sorting is labeled as 0,1, 2…
See the difference in the example below:
import pandas as pd
#A list to be used for Data Frame
emp_data = [ ['Emp1', "Mike", 5600],
['Emp2', "Michelle", 4750],
['Emp3', "Ben", 6500],
['Emp4', "Shabee", 3600],
['Emp5', "Mina", 3250]
]
#Creating data frame
df_emp = pd.DataFrame (emp_data, columns = ['ID', 'Name', 'Salary'])
print("Sort results with ignore_index=False (default value)")
print(df_emp.sort_values(by=['Name', 'Salary'], ignore_index=False))
print("Sort results with ignore_index=True")
print(df_emp.sort_values(by=['Name', 'Salary'], ignore_index=True))
Output:
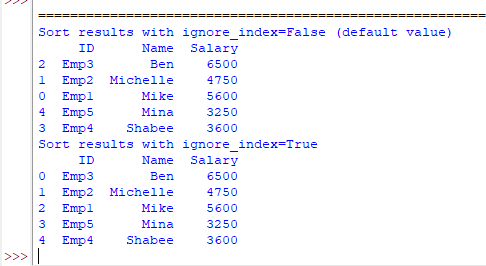
Reference:
https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.sort_values.html
