The Python break statement is used to terminate the for or while loops. Normally, the loop ends as the testing condition fails. However, in certain scenarios, you may require ending the loop earlier e.g. if the desired task is accomplished, etc.
A few points about the break statement:
- The execution moves to the next line of code outside the loop block after the break statement.
- If the break statement is used in an inner loop, its scope will be inner loop only. That is, the execution will move to the outer loop after exiting the inner loop.
- The break statement can be used with for or while loops.
Tip: The continue statement is also used in loops to omit the current iteration only. Learn more about the continue statement.
See the next section for the examples of using break Python statement.
A break statement example with for loop
A list of numbers is created in the example. By using for loop, its items are displayed. However, as it reaches item with value 6, the break statement will execute and terminate the loop. Have a look:
#A demo of break statement with for loop
lst_num = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
for x in lst_num:
if x == 6:
break
print("List item: " ,x)
print("The loop terminated at item 6")

An example of break in the inner for loop
For this example, an inner loop is also used and break statement is applied there. The outer loop iterates through a numeric list while the inner loop to string list.
For each item of the outer loop, the inner loop will execute. An if statement is used to check the current item value and if it is equal to ‘c’, the break statement will execute and terminate the inner loop while execution gets back to the outer loop:
#A demo of break statement with for loop
lst_num = [2, 4, 6]
lst_str = ['a' ,'b', 'c']
for x in lst_num:
print("Number item: " ,x)
for y in lst_str:
if y == 'c':
break
print(" String item: " ,y)
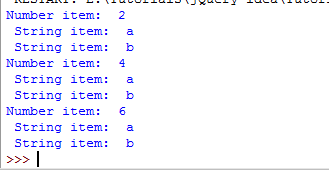
You can see, all items of the outer loop are entertained while inner loop executed three times and always terminated as it reached item ‘c’.
An example of using break with while loop
The following example shows how you may use the break statement with while loop.
#Using break with while loop example num = 5 while num <= 30: if num == 25: break print (num) num = num + 5
The output of the program is:
5
10
15
20
>>>
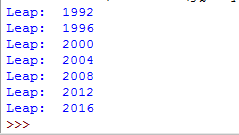
A continue statement example
Just for showing the difference between the break and continue statement, have a look at this example where leap years from 1992 to 2018 are displayed. A range is created for years and used in the for loop.
For the non-leap years, the loop will omit the current iteration by using continue statement while for the leap year, it will display the year. Have a look:
#Demo to show difference between continue and break
for years in range(1992, 2018):
if years % 4 == 0:
print("Leap", years)
continue
For more on continue statement, visit the tutorial.
