The sin() function:
- Takes an argument (x = number)
- and returns its sine in radians.
- It’s the part of math module, so this function cannot be used directly.
- You have to import the math module in your Python program – as shown in the examples below.
- To get the result in degrees, you may use the radians() function along with sin() as shown in the example in the later section of this tutorial.
Syntax of sin() function
This is how the sin() function is used:
sin(x)
For example:
math.sin(3)
See the examples below for complete code.
An example of sin() function
The example below shows using the sin() function to get the sine of a few numbers. We will get the sine in radians for 30, 45 and 60:
#A demo of sin() function
from math import sin
sine_30 = sin(30)
sine_45 = sin(45)
sine_60 = sin(60)
print ("The sine of 30 = ", sine_30)
print ("The sine of 45 = ", sine_45)
print ("The sine of 60 = ", sine_60)
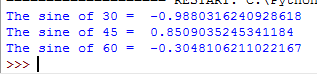
The result:
In the above example, we used the shorthand for using the sin() function. This code will produce the same result:
import math
sine_30 = math.sin(30)
sine_45 = math.sin(45)
sine_60 = math.sin(60)
print ("The sine of 30 = ", sine_30)
print ("The sine of 45 = ", sine_45)
print ("The sine of 60 = ", sine_60)
The result:
The sine of 30 = -0.9880316240928618
The sine of 45 = 0.8509035245341184
The sine of 60 = -0.3048106211022167
How to get sine in degree?
You might be wondering why these answers are different than using a calculator for getting the sine of a number? This is because Python sin () function returns sine in radians.
The math module has another function radians() that you may use for converting the radians to degrees.
The example below uses the same values as in the above examples and also use the radians() function for converting the returned result by sin() function and get the sine values in degree:
import math
sine_30 = math.sin(math.radians(30))
sine_45 = math.sin(math.radians(45))
sine_60 = math.sin(math.radians(60))
print ("The sine of 30 in degree = ", sine_30)
print ("The sine of 45 in degree = ", sine_45)
print ("The sine of 60 in degree = ", sine_60)
The output:
The sine of 30 in degree = 0.49999999999999994
The sine of 45 in degree = 0.7071067811865475
The sine of 60 in degree = 0.8660254037844386
Rounding the result example
The example below uses three functions together; sin(), radians() and round(). The round function will round the result returned by radians() function to single precision. See the code and output:
import math
sine_30 = round(math.sin(math.radians(30)),1)
sine_45 = round(math.sin(math.radians(45)),1)
sine_60 = round(math.sin(math.radians(60)),1)
print ("The sine of 30 in degree with single precision = ", sine_30)
print ("The sine of 45 in degree with single precision = ", sine_45)
print ("The sine of 60 in degree with single precision = ", sine_60)
The output of the above code is:
The sine of 30 in degree with single precision = 0.5
The sine of 45 in degree with single precision = 0.7
The sine of 60 in degree with single precision = 0.9
Learn more about the round function in its tutorial: Python round function.
