In Python, you may convert a date to string that is in an easily readable format to the users in different ways.
Being able to format date by string conversion is important as the default way of displaying the date, for example, as using the now() function of datetime module returns as follows:
2018-12-13 17:58:01.816168
So, what if you want to display the date like these:
13/12/2018 13 Dec 2018 13 December, 18 Thursday, 13 Dec 2018
And so on.
You may use the datetime module’s built-in function strftime(). The strftime() function is also available in date and time modules for creating the string representing the date in the required format.
In the section below, a few examples of strftime() function are given in different date formats. You may also see the examples of using format() function for converting date into string.
An example of datetime to string by strftime()
In this example, we will get the current date by using the now() function of the datetime module and then convert this to a string by strftime() function in the following format:
Full day name, day number Month Year
See the code and output below:
#Date conversion to string
import datetime
dt_date = datetime.datetime.now()
print ("The Current date is:" ,dt_date)
print("In specified format:", dt_date.strftime("%A, %d %b %Y"))
The output:
The Current date is: 2018-12-14 18:30:40.152677
In specified format: Friday, 14 Dec 2018
The example with specified date arguments
In this example, the date values are given in the datetime() function. The datetime() function belongs to datetime module. This is followed by using the strftime() for creating the string representing that date:
#Date conversion to string example
import datetime
dt = datetime.datetime(2017, 4, 16, 0, 0)
date_string = dt.strftime('%m/%d/%Y')
print("The string representation of date in mm/dd/yyyy:", date_string)
The output:
The string representation of date in mm/dd/yyyy: 04/16/2017
You may see the list of directives for date formatting here.
String representation of date and time example
In this example, I also used time related directives for showing the current time along with the date in dd/mm/yy format. The complete date and time should display like this:
20/08/17 11:25 50
Have a look at the code and output:
#Date conversion to string example
import datetime
current_date_time = datetime.datetime.today()
dt_string = current_date_time.strftime('%d/%m/%y %I:%M %S %p')
print("Date/Time in dd/mm/yy Hour:Min Second AM/PM:", dt_string)
The output as this code is executed:
Date/Time in dd/mm/yy Hour:Min Second AM/PM: 15/12/18 12:53 29 PM
Note: %I yields hours in 01,02,…12 format while %H in 01,02, ….12, 23 format.
The example of using format() function
As mentioned earlier, you may also use format() function with the date directives for getting the string representation of date and time.
The directives are provided within curly brackets preceded with the colon mark.
The example below shows displaying date and time in various formats using the format() function with different directives:
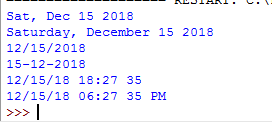
#Date conversion to string example
import datetime
cur_dt1 = datetime.datetime.today()
dt_str1 = '{:%a, %b %d %Y}'.format(cur_dt1)
dt_str2 = '{:%A, %B %d %Y}'.format(cur_dt1)
dt_str3 = '{:%m/%d/%Y}'.format(cur_dt1)
dt_str4 = '{:%d-%m-%Y}'.format(cur_dt1)
dt_str5 = '{:%m/%d/%y %H:%M %S}'.format(cur_dt1)
dt_str6 = '{:%m/%d/%y %I:%M %S %p}'.format(cur_dt1)
print(dt_str1)
print(dt_str2)
print(dt_str3)
print(dt_str4)
print(dt_str5)
print(dt_str6)
The output: