Ways to Check File Existence in Python
You may use different ways to check if the file exists or not in Python programs.
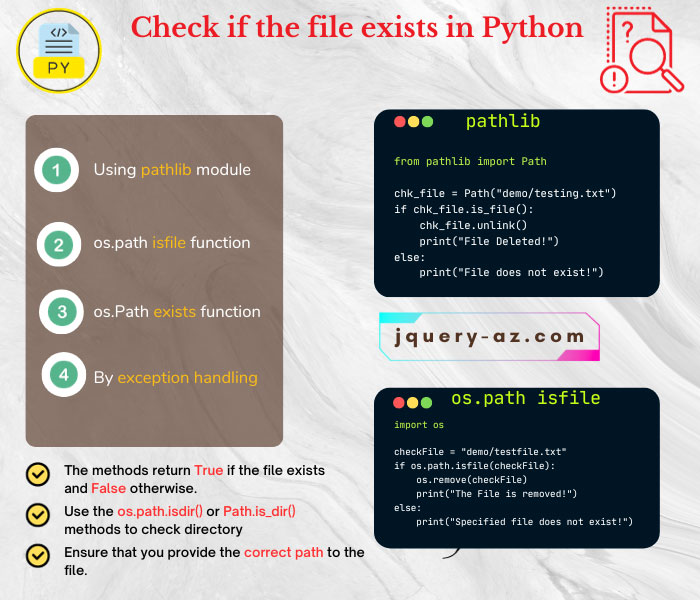
In this tutorial, we covered:
- Using pathlib module
- Using os.path isfile function
- By os.Path exists function
- By exception handling
This may be required for different reasons. For example, you want to remove a file, and before that make sure if that file exists or not. Because, if the file does not exist in the specified path then an exception may be raised.
Apart from that, it is generally good practice to ensure things and keep them in control.
First way: Using pathlib module
The pathlib module is appropriate for different operating systems by offering classes representing filesystem path with semantics. This is the object-oriented approach as compared to using the os module (coming up in the next section).
- The main class in the pathlib is Path which has a function is_file().
- The is_file() function returns True if the Path is pointing to a regular file.
- Similarly, if you are using a symbolic link that points to a regular file then it returns True.
- If the path does not exist, it returns False.
- So, pathlib.Path can be a better way of checking if a file exists or not.
The following example shows how:
#A demo of checking if file exists by pathlib.path
from pathlib import Path
chk_file = Path("demo/testing.txt")
if chk_file.is_file():
chk_file.unlink()
print("File Deleted!")
else:
print("File does not exist!")
In the above program, we set the path and then checked if the file exists or not. If the file is found, it is deleted by using the unlink() function. If the file is not found, an appropriate message is displayed.
Way 2: Using os.path isfile function
The second way of checking if the file exists or not is using the os module’s path class.
The Path class has a method isfile that returns True if the path is an existing regular file.
In the following example, again I checked the file path and removed it if found by using the isfile function.
#The example of os.path isfile function
import os
checkFile = "demo/testfile.txt"
if os.path.isfile(checkFile):
os.remove(checkFile)
print("The File is removed!")
else:
print("Specified file does not exist!")
Third way: The os.Path exists function
The os.path has another function called exists() that returns True if the specified path is an actual file.
- The exists() function takes an argument which is the path of the file.
- The function returns False if the path does not exist.
- It also returns False in some platforms if the requested file is not granted to execute os.stat().
The example below shows how to use the exist() function to check if files exist or not:
#The example of os.path exists()
import os
filePath = "demo/tst-exist.txt"
if os.path.exists(filePath):
os.remove(filePath)
print("The File is removed!")
else:
print ("File not found!")
Fourth way: By exception handling
In this way, you may avoid crashing a program if the specified file is not found. As you execute a command to open a file and this is not found, the program raises an error: FileNotFoundError.
For example:
filepath = “‘demp/test.txt ”
file_tst = open(filepath)
file_tst.close()
If test.txt does not exist, it will raise the following error:
You may handle this error in the try-except block and show an appropriate message if the file does not exist.
The following program shows how:
#check file by try-except
filepath = "demp/test.txt"
try:
file_tst = open(filepath)
file_tst.close()
except FileNotFoundError:
print('File does not exist')
If the specified file is not found, the program should display the following message without crashing:
