What is Java charAt method?
- The charAt(int) method returns the character in the specified string for a given index number.
- The index of string starts at zero.
- For example, consider this string:
You want to know the character at the 6th index position in that string by using charAt method:
String strCharat = "Hello World Java";
System.out.println("The character at 6 index is: " +strCharat.charAt(6));
Syntax of using charAt Java method
A few points about the string charAt method:
| parameter | The charAt takes a parameter which is an int type. |
| Returns | The method returns the character as char for the given int argument.
The int value specifies the index that starts at 0. |
| Length requirement | The index range must be between 0 to the length of string -1. |
| Error | If the index value is greater than the string length or a negative number, an error IndexOutOfBoundsException occurs. |
| specified by | The charAt method is specified by CharSequence. |
The example of using charAt method
In the following example, the Java charAt method is used to return the character in a string.
I will use the same string as in the introductory section. Let us see which characters occur at the index 6 and 12:
public class demo_tst {
public static void main(String []args) {
//How to use charAt method
String strCharat = "Hello World Java";
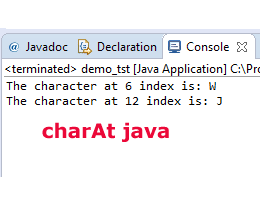
System.out.println("The character at 6 index is: " +strCharat.charAt(6));
System.out.println("The character at 12 index is: " +strCharat.charAt(12));
}
}
The output:
The character at 6 index is: W
The character at 12 index is: J
A program to answer if certain characters exist in a string?
By using charAt method, this program will output if a vowel character occurs at the start of the specified string.
For that, a string is entered by the user and the program will check for these characters. For taking the user input, the Scanner class is used:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo_tst {
public static void main(String []args) {
Scanner readInput = new Scanner(System.in); // Reading from System.in
System.out.println("Enter a String: ");
String str_charAt = readInput.next();
char chr = str_charAt.charAt(0);
if (chr == 'a' || chr == 'e' || chr == 'i' || chr == 'o' || chr == 'u')
System.out.println("Found the following vowel as first character: " +chr);
}
}
See the output of the tried strings:
Enter a String: amazing Found the following vowel as first character: a Enter a String: unlucky Found the following vowel as first character: u Enter a String: mango Enter a String: oranges Found the following vowel as first character: o
What if the given index is greater than the length of the string?
As mentioned earlier, if you provide a negative number or greater than the string length then an error occurs:
public class demo_tst {
public static void main(String []args) {
//How to use charAt method
String strCharat = "charAt method";
System.out.println("Index 4 = " +strCharat.charAt(4));
System.out.println("Index 7 = " +strCharat.charAt(7));
System.out.println("Index 15 = " +strCharat.charAt(15));
}
}
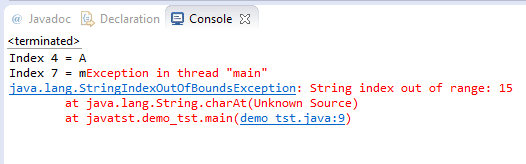
For index 15, the program generated StringIndexOutOfBoundsException error with the description: String index out of range: 15.
The indexOf method
The indexOf method returns the index number of the given character in the specified string. For example, if we have a string:
This is how you may use the indexOf method for getting ‘J’ index number:
Java program:
public class demo_tst {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String strIndOf = new String("indexOf method in Java");
int x;
x = strIndOf.indexOf('J');
System.out.print("The indexOf 'J' is: " + x );
}
}
The output: