The REPLACE function in SQL is used for replacing all occurrences of the search term in the specified string to the new given string value.
For example, we have a string:
“MS SQL Server 2000”
We need to change it with
“MS SQL Server 2017”
This is how the replace function can do that:
REPLACE(‘MS SQL Server 2000’, ‘2000’, ‘2017’);
The REPLACE takes three parameters as follows:
- The first parameter is the source string.
- In the second parameter, the string or sequence of characters to replace is specified.
- The third parameter specifies string or sequence of characters to be replaced with
An example of REPLACE function
In this example, a simple string is specified in the REPLACE function. In the string, 2000 is replaced by 2017 as follows:
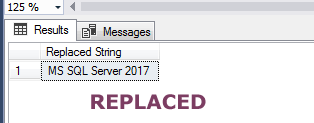
Query:
SELECT REPLACE('MS SQL Server 2000', '2000', '2017')
AS "Replaced String";
The result:
Note: The REPLACE function is case-insensitive in MS SQL Server. That is, the letter ‘C’ and ‘c’ has the same meaning. However, in MySQL, the REPLACE is case-sensitive.
Using a table column with REPLACE function
This example shows using the REPLACE function with a table column. We have a dummy table, sto_products, that stores product information including quantity.
See how a numeric column value is replaced and original and replaced values are displayed in the recordset:
The Query:
SELECT *, REPLACE(prod_quantity, 150, '150 Items') AS "Replaced Quantity" FROM sto_products WHERE prod_id=1;
The result:
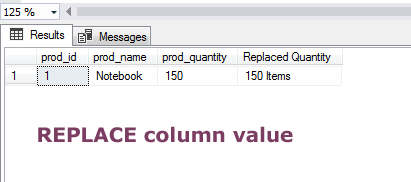
You can see, the numeric column value can also be specified in the REPLACE function.
What happens for multiple occurrences?
As mentioned earlier, the REPLACE function replaces all the occurrences of the matched string in the specified string. See a demo below where letter T is replaced by R:
SELECT REPLACE('This is REPLACE Tutorial', 'T', 'R')
AS "Replaced String";
The resultant string:
“Rhis is REPLACE RuRorial”
You may also notice the REPLACE is not case sensitive. It also replaced ‘t’ with ‘R’ in above string.
Mixing the REPLACE and CONCAT functions
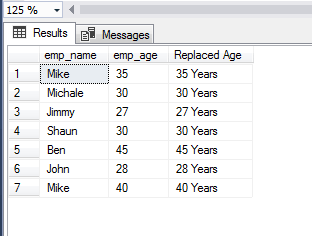
This is an interesting use of the REPLACE function where I am going to use CONCAT function as well. In the sto_employees table, I used dummy records of employees including name and age. The age contains numeric values e.g. 35, 40.
By using REPLACE function, I will retrieve the recordset for employee names and age with only digits and by using CONCAT the third column is also displayed. This will display the age with “years” for each employee as follows:
The CONCAT/REPLACE query:
SELECT emp_name, emp_age, REPLACE(emp_age,emp_age, CONCAT(emp_age, ' Years')) AS "Replaced Age" FROM sto_employees;
The resultset:
The example of REPLACE function with UPDTAE statement
You may also use the REPLACE function with UPDATE statement for modifying the records permanently. Although, there are other ways of doing it; you may also do it by REPLACE function that in some situation may be helpful.
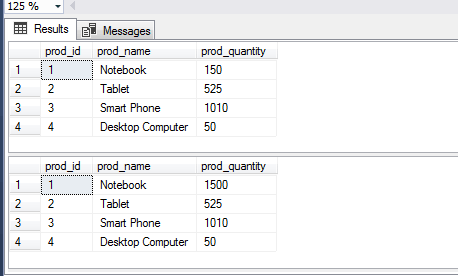
See the query below for an idea of using the REPLACE function. In the query, I have updated the product price which is a numeric column:
UPDATE sto_products set prod_quantity = REPLACE(prod_quantity, 150, 1500) WHERE prod_name = 'Notebook';
The result before and after UPDATE/REPLACE:
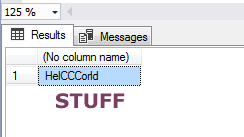
Difference between STUFF and REPLACE functions
The STUFF function is also used for replacing the specified string with new given string. As such, the REPLACE function replaces all matched occurrences in the specified string, on the other hand, the STUFF function replaces from the given starting position.
So, if you are not looking to replace all occurrences and know the position to start replacing in the specified string then use the STUFF function as shown in the example below:
The STUFF query:
SELECT STUFF ( ‘Hello World’ , 4 , 4 , ‘CCC’ );
The result: