The SQL BETWEEN operator is used to specify a range to test.
- You may use BETWEEN operator with SELECT statement for retrieving data for the given range.
- The BETWEEN operator can also be used in the DELETE, UPDATE and INSERT statements for specifying the range.
- You may specify the range of numbers, two dates, and text as using the BETWEEN SQL.
- The range values are inclusive, for example:
BETWEEN 10 AND 20
This is equivalent to
>=10 AND <=20
See the examples below for learning how to use the BETWEEN operator for numeric, date and text columns.
The example of BETWEEN two dates
In the first example of using BETWEEN operator, I am using employees table that stores joining date of employees along with other basic data.
By using the BETWEEN operator, I have provided two dates for returning the data for employees:
Query:
SELECT * FROM sto_employees WHERE join_date BETWEEN '01-01-2016' AND '12-12-2016';
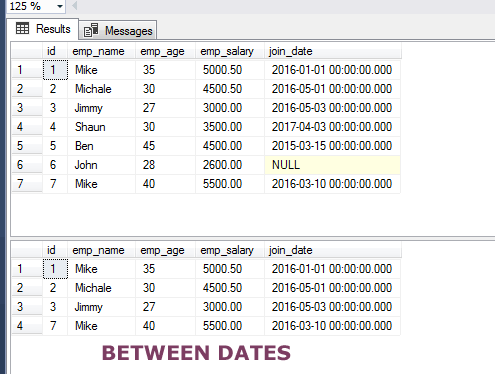
The first query fetched the complete data in the table while the second one retrieved by using the BETWEEN operator with two dates range.
You may also notice, the specified dates are inclusive.
Using NOT with BETWEEN operator
The NOT BETWEEN condition returns the result that is outside of the given range (inclusive of specified values).
Let us use the NOT BETWEEN in our above example table and see what it returns:
The query:
SELECT * FROM sto_employees WHERE join_date NOT BETWEEN '01-01-2016' AND '12-12-2016';
Result-set:
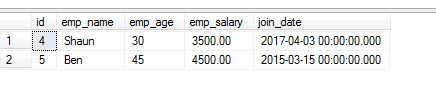
If you look at the first example graphics with complete table data, you can see this query returned those records that did not return in above BETWEEN query. Moreover, the join_date with the NULL value is not returned in both cases.
Note: You may test these BETWEEN examples with dates on MySQL and MS SQL Server.
The example of using numeric values in BETWEEN operator
The following query shows using a range of two numbers in the BETWEEN clause. The query returns the records of employees from 3 to 7 IDs of employees.
The Query with numbers:
SELECT * FROM sto_employees WHERE id BETWEEN 2 AND 5;
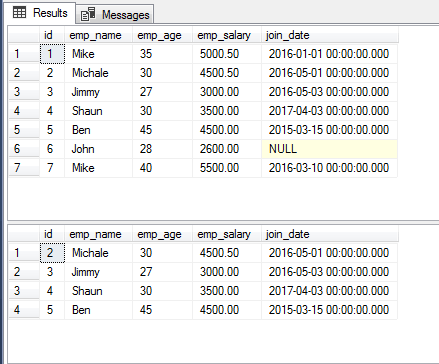
You can see, ID 2 and 5 also included in the fetched results.
Using multiple BETWEEN with OR operator
You may also use multiple BETWEEN clauses in case multiple ranges are required to retrieve from the table. The following example used two BETWEEN clauses with OR clause for employee ID:
The Query:
SELECT * FROM sto_employees WHERE id BETWEEN 1 AND 3 OR id BETWEEN 5 AND 7;
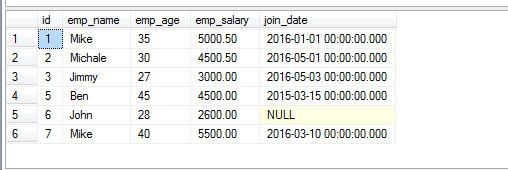
Similarly, you may specify different columns in multiple BETWEEN clauses.
Using text values in BETWEEN operator
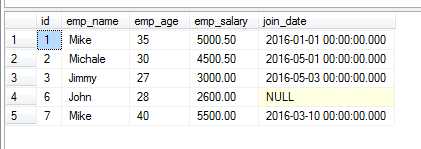
Now, let us fetch the records of employees based on employee names in the BETWEEN operator. See the query and output in the example below:
SELECT * FROM sto_employees WHERE emp_name BETWEEN 'Jimmy' AND 'Mike';
The result:
Using the DISTINCT clause with BETWEEN operator
This example shows using the DISTINCT clause with BETWEEN operator:
SELECT DISTINCT emp_name FROM sto_emp_salary_paid WHERE emp_id BETWEEN 2 AND 5;
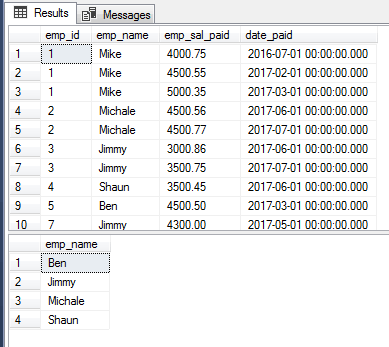
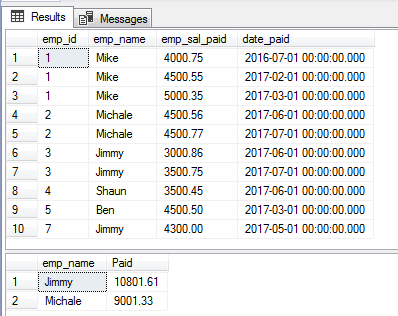
The example of BETWEEN with GROUP BY and HAVING clause
Until now, we have used the BETWEEN operator with the WHERE clause in SQL. You may also use BETWEEN operator in the GROUP BY clause and specify a condition with HAVING clause.
The following query returns the SUM of paid salary from the sto_emp_salary_paid table and displays only those records which SUM is between the range of 5000 to 12000. See how this combination is used:
The query:
SELECT emp_name, SUM(emp_sal_paid) As "Paid" FROM store_db.dbo.sto_emp_salary_paid GROUP BY emp_name HAVING SUM(emp_sal_paid) BETWEEN 5000 AND 12000;
The complete table data and query result: