
An Introduction to C++ String Find Function
- The string find() function in C++ is used to find a substring in the given string.
- The find() function belongs to the C++ string class.
- We must include <string> in the header section (see the programs below)
- For example, we have the string “This is C++ tutorial”.
- We want to find out if the above string contains the word “tutorial” or not.
- In the find() function of C++, we can specify that string and provide the word “tutorial”.
- The find method returns the position of the word if found.
- If the position of the given word/character is found – that means the word exists – otherwise, it is not.
- If the searched string is not found the find method returns string::npos. npos is the static member constant value with the greatest value for an element of size_t.
Syntax of using C++ find() function
Following is the syntax for using the find() function:
Following are the parameters description of the find function:
| Parameter | Description |
| Str | The string object. The string you want to search in. |
| Seq | It’s the sequence of characters that you want to search in the str. |
| Pos |
|
| Count |
|
Now let us look at a few examples of using the string find function with one or more parameters.
An example of C++ find with a single parameter
In this example, we only used the required parameter in the find() function. We have created a string (str1) and used it with the find method.
Another string variable is declared (str2) which is used as the sequence to search in the find method. See the code and output:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//Creating string object to search in
string str1 = "This is C++ tutorial";
//substring or seq to search in str1
string str2 = "tutorial";
//Using find function
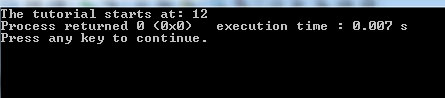
cout <<"The tutorial starts at: " << str1.find(str2);
}
Output:
What if a given sequence occurs twice or more?
In this example, we searched for a character ‘s’ in the given string. It occurs twice in the sentence. See what it outputs:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//Creating string object to search in
string str1 = "Hang on, I am coming!";
//substring or seq to search in str1
string str2 = "o";
//Using find function
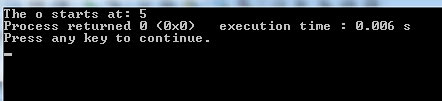
cout <<"The o starts at: " << str1.find(str2);
}
Output:
An example with sequence and position parameter
- In the program below, we used two parameters in the find function.
- The first is the sequence (just like the above example i.e. str2) and the second is the position parameter.
First, have a look at the code and output below:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//Creating string object to search in
string str1 = "Have a nice day!";
//substring or seq to search in str1
string str2 = "nice";
//Using find function with position parameter
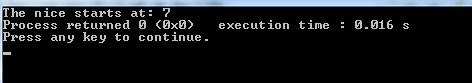
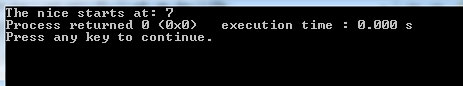
cout <<"The nice starts at: " << str1.find(str2, 3);
}
First output as we set position 3:
When we set position 8:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//Creating string object to search in
string str1 = "Have a nice day!";
//substring or seq to search in str1
string str2 = "nice";
//Using find function with position parameter
cout <<"The nice starts at: " << str1.find(str2, 8);
}
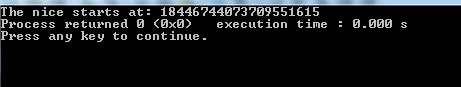
- As sequence/word “nice” starts at position 7. In the first program, we see the output as 7.
- However, in the second program, we set the searching position to start at 8.
- As the find function was unable to find the word “nice” from position 8, so it returned string::npos. Which is described in the first section.
What if the sequence occurs twice?
We will search for the letter ‘o’ in this example. It occurs twice in the given sentence. However, the position is given so the first occurrence should be bypassed.
Let us see the output:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//Creating string object to search in
string str1 = "Hang on, I am coming!";
//substring or seq to search in str1
string str2 = "o";
//Using find function
cout <<"The o starts at: " << str1.find(str2, 6);
}
Output:
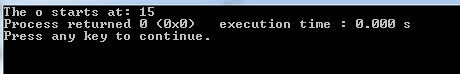
You saw though the first occurrence is at position 5, it did not return. The reason is we set position 6. So it returned the next occurrence of ‘s’ which is 15.
Using all three parameters example
In the following program, we also used a third optional parameter i.e., count. See the code and output below:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//Creating string object to search in
string str1 = "Have a nice day!";
//Using find function with position and count parameter
cout <<"The nice starts at: " << str1.find("nicee", 7, 3);
}
Output:
`
