What is C++ OR operator
- OR is a logical operator in C++
- The OR is denoted by || (two pipe signs)
- The OR is used to evaluate two statements
- If both statements are true, it returns 1 i.e. true
- If one statement is true and the other is false, it returns 1 i.e. true
- In case, both statements are false – it reruns 0 i.e. false
- Unlike the AND operator (&&) that reruns false if any of the statement is false
A simple example of using OR (||) operator
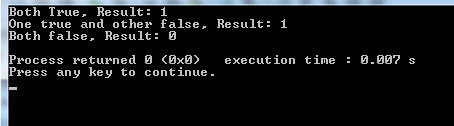
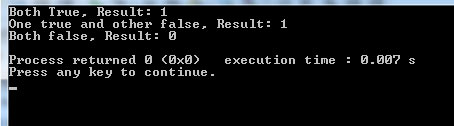
In this example, we have two int type variables. We will check its equality with the || operator and display three results. See the C++ program below:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
cout <<"Both True, Result: " <<(a == 5 || b == 10) <<"\n";
cout <<"One true and other false, Result: " <<(a != 5 || b == 10) <<"\n";
cout <<"Both false, Result: " <<(a != 5 || b != 10) <<"\n";
// 1
}
Output:
Using OR operator in if statement examples
The following short snippet of code in C++ shows using OR logical operator (||) in the if statement.
The three programs below show the result when:
- both conditions are true
- one condition is true and the other is false
- both are false
Program 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 5;
int y = 10;
if ( (x <= 5 || y >= 10) )
{
cout << "True";
}
else
{
cout<<"False";
}
cout<<"\n\n";
}
Output:
True
As the value of x is less than or equal to 5 and the value of y is greater than or equal to 10, so both conditions are true and the output is True.
Program 2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 5;
int y = 10;
if ( (x > 5 || y >= 10) )
{
cout << "True";
}
else
{
cout<<"False";
}
cout<<"\n\n";
}
Output:
True
As the value of x is not greater than 5, our first condition is false. However, the y value is greater than or equal to 10, so it’s true; so end result is true.
Program 3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 5;
int y = 10;
if ( (x > 5 || y < 10) )
{
cout << "True";
}
else
{
cout<<"False";
}
cout<<"\n\n";
}
Output:
False
As neither value of x is greater than 5 nor the value of y is less than 10 – so both conditions are false. As a result, the else part executed that displayed “False”.
Using two OR operators examples
We are extending our above example to show you using the two OR operators in a single if statement.
For that, we have a third char-type variable with an initial value. It’s value is also checked in the if statement as follows:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 5;
int y = 10;
char chr = 'y';
if ( (x > 5 || y < 10 || chr == 'y') )
{
cout << "True";
}
else
{
cout<<"False";
}
cout<<"\n\n";
}
Output:
True
Although, the x and y conditions are false, however, the chr value is ‘y’, so it is true. The end result is True.