For string comparison in Java, you may use:
- equals() method
- compareTo() method
There are some differences between the two methods – return values and others as you compare objects/strings.
Both of these methods are explained below with examples.
Java equals() method
- In the context of string comparison, the equals method indicates if this string is equal to the other string.
- The use of equals() method is broad and basically, it checks if this object is equal to the specified object.
- The object can be a string or other type.
This is how equals() method can be used:
public boolean equals(Object obj)
| The given string is equal | The equals method returns true if the given string is equal to this string. |
| null argument | If the argument is null, it returns false e.g. str.equals(null). |
| Returns false | If another string object does not match the same sequence of characters of this object, it returns false. |
See the following section for examples with different possibilities as using the equal Java method.
An example of equals() method
For this example, three string objects are created and assigned values.
All strings apparently are the “same”, however, in the string1 and string2, the only difference is the case letters for two words. String1 and string3 are exactly the same.
The equals method is used for string comparison and its returned results are displayed as follows:
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
String Str1 = "Equals to compare Strings";
String Str2 = "equals to compare strings";
String Str3 = "Equals to compare Strings";
System.out.println("Str1 and Str2 are equal? " + Str1.equals(Str2));
System.out.println("Str1 and Str3 are equal? " + Str1.equals(Str3));
}
}
Output:
Str1 and Str3 are equal? true
The first comparison returned false and the second as true, because, “String” and “string” are two different words.
The compareTo method
Generally speaking, the Java compareTo method compares this object (string in our case) with the specified object for order. The syntax of using the compareTo() method is:
- The method returns an integer, unlike a Boolean in the case of the equals() method.
- If this object is less than the specified object then it returns a negative number.
- If it is equal to the specified object then it returns zero.
- The compareTop() returns a positive integer if this object is greater than the specified object.
- The equals() tells the equality of two strings whereas the compareTo() method tells how strings are compared lexicographically.
So in our context of the strings, we may conclude as follows:
For string comparison of str1 and str2:
- str1 == str2 returns 0
- str1 < str 2 returns a negative integer
- str1 > str 2 returns positive integer
An example of string comparison by compareTo() method
For this example, three string objects are created and compared as follows:
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
String str1 = "Banana";
String str2 = "Mango";
String str3 = "Banana";
System.out.println("str1.compareTo(str2) Returned: " + str1.compareTo(str2));
System.out.println("str3.compareTo(str1) Returned value: " + str3.compareTo(str1));
System.out.println("str1.compareTo(str3) Returned value: " + str1.compareTo(str3));
}
}
Output:
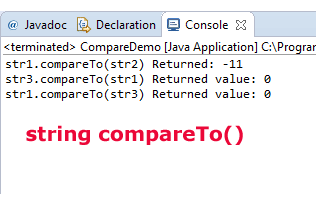
What if the specified object is null?
If you try to compare a string that is null the compareTo method throws a NullPointerException error. See the following example:
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
String str1 = "Java";
String str2 = null;
System.out.println("str1.compareTo(str2) Returned: " + str1.compareTo(str2));
}
}
The output:
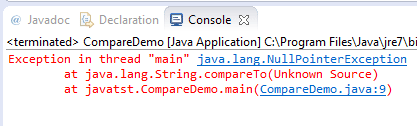
In the case of the equals() method, if the compared string is null, it simply returns false:
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
String Str1 = "comparing null string";
String Str2 = null;
System.out.println("Str1 and Str2 are equal? " + Str1.equals(Str2));
}
}
The output:
