The LEFT JOIN combines two tables and returns the matched records from both tables and unmatched records from the “left” table as well.
As such, one table is given after the “FROM” clause while the other after the JOIN clause; the table specified in the FROM clause is left table and the table after the LEFT JOIN clause is right table. The LEFT JOIN returns all rows from the “left” table.
The values for the right table are filled with “NULL” values that are unmatched. The examples after the syntax make it clearer that how MySQL LEFT JOIN works.
Syntax for using MySQL LEFT JOIN
This is how the MySQL LEFT JOIN is used:
SELECT tab1.col1, tab2.c1,.... FROM left_table t1 LEFT JOIN right_table t2 ON tab1.col1 = tab2.col1;
An example of MySQL LEFT JOIN
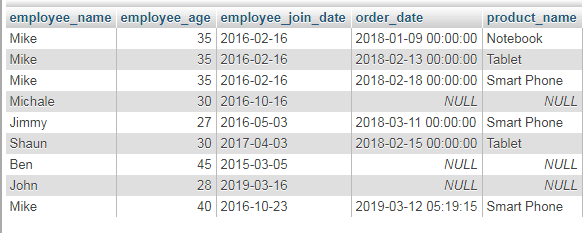
In this example, I am using two tables for explaining how LEFT JOIN works. We have an employee table that stores basic information about the employees while the second table is the orders table that stores order information along with the ID of the employee who takes that specific order.
The common key in these two tables is employee id that is used as follows:
The query:
SELECT employee_name, employee_age, employee_join_date, order_date FROM tst_employees LEFT OUTER JOIN tst_orders_customers ON tst_employees.id = tst_orders_customers.emp_id
Note: You may simply use LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN as well.
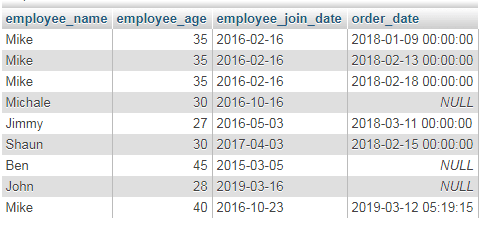
The example of using table alias
As shown in the syntax of LEFT JOIN, you may also use table name alias instead of full names as specifying the common keys. The example below returns the same result as in the above example, except I used the table alias:
The query:
SELECT employee_name, employee_age, employee_join_date, order_date FROM tst_employees TE LEFT JOIN tst_orders_customers TOr ON TE.id=TOr.emp_id;
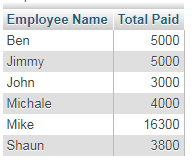
An example of using GROUP BY clause with LEFT JOIN
The example below uses the MySQL GROUP BY clause with the LEFT JOIN. Again, employees and orders tables are used and the query returns total paid salaries of those employees whose records exist in orders table:
The Query:
SELECT employee_name AS "Employee Name", SUM(employee_salary) As "Total Paid" FROM tst_employees TE LEFT JOIN tst_orders_customers TOr ON TE.id=TOr.emp_id GROUP BY TE.employee_name;
The result:
Adding HAVING clause example
Similarly, you may add the HAVING clause for filtering the rows returned with GROUP BY clause. See the combination of LEFT JOIN, GROUP BY and HAVING clauses:
Query:
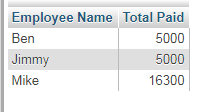
You can see in the above graphic that the records of those employees are returned whose aggregated salary is greater than 4000.
Using multiple LEFT JOIN example
The following query uses multiple LEFT JOINs that combines the data of three tables. In addition to the above two tables, the products table is also included in the query as shown below:
SELECT employee_name, employee_age, employee_join_date, order_date, product_name FROM tst_employees TE LEFT JOIN tst_orders_customers TOr ON TE.id=TOr.emp_id LEFT JOIN tst_products TP ON TP.product_id = TOr.prod_id;
The result: