Purpose of Random class in C#
A few main points about the Random class:
- The Random class represents pseudo-number generator.
- A mathematical algorithm is used for generating a random number.
- The random class uses the modified version of Donald E. Knuth’s subtractive random number generator algorithm.
- You may use the Random class after including the reference for the System namespace.
An example of generating a random number
In this example, five int (byte) numbers are generated randomly.
- First, a byte-type array is declared with four elements.
- Then, a random object is created and NextBytes method of the Random class is used to generate four random numbers.
- Finally, we used a foreach loop to display the random numbers as follows:
using System;
class Random_Example
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
byte[] randBytes = new byte[4];
rand.NextBytes(randBytes);
Console.WriteLine("Generated Numbers Are:");
foreach (byte randVal in randBytes)
Console.Write("{0, 4}", randVal);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
The output as I executed this code:
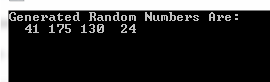
The numbers should vary as you execute this code every time.
Using the Next method for generating int random numbers within a range
The following example shows using the Next method of the Random class and generating random numbers based on provided ranges.
For example, the first random number is generated between 1 – 100. The second is between 100 to 400 while the fourth is from 1000 to 10000.
The Code:
using System;
class Random_Num_Next
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
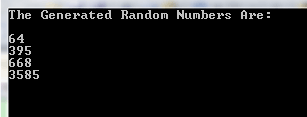
Console.WriteLine("The Generated Random Numbers Are: \n");
Console.WriteLine(rand.Next(1, 100));
Console.WriteLine(rand.Next(100, 500));
Console.WriteLine(rand.Next(501, 1000));
Console.WriteLine(rand.Next(1000, 10000));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
The example of creating double-type random numbers
In the example below, we have an array of the double type with three elements.
The NextDouble method of the Random class is used as follows:
using System;
class Random_Example
{
static void Main()
{
Random dbl_rand = new Random();
double[] arr_rand_dbl = {
dbl_rand.NextDouble(),
dbl_rand.NextDouble() ,
dbl_rand.NextDouble()
};
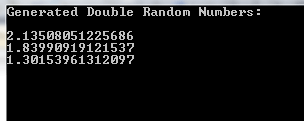
Console.WriteLine("Generated Double Random Numbers:\n");
foreach (double rand_result in arr_rand_dbl)
{
Console.WriteLine(rand_result);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
You may also use:
dbl_rand.NextDouble() + 1,
dbl_rand.NextDouble() – 2,
dbl_rand.NextDouble() + 3
That means you may also specify a number if you want to get the random number bigger or smaller.
An example of generating five random numbers within a range
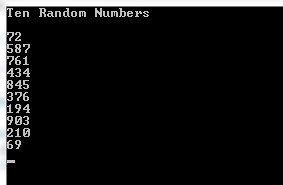
The following example shows generating ten random numbers within the range of 1 and 1000. A for loop is used for that purpose as shown below:
using System;
class Random_Example_Ten
{
static void Main()
{
Random range_rand = new Random();
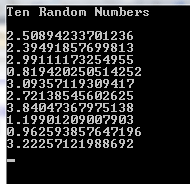
Console.WriteLine("Ten Random Numbers \n");
for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++)
Console.Write(range_rand.Next(1, 1000) + "\n");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
The output as this code is executed:
Generating ten random floating numbers
This example shows generating ten floating random numbers by using the NextDouble() method in the for loop. The random numbers are within the range of 1 and 4:
using System;
class Random_Example_Ten_Float
{
static void Main()
{
Random range_rand_dbl = new Random();
Console.WriteLine("Ten Random Floating Numbers \n");
for (int z = 1; z <= 10; z++)
Console.Write(range_rand_dbl.NextDouble() * 4 + "\n");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}