MySQL has two types of IFs: one is the IF statement while the other is the IF function. In this tutorial, I will explain the difference and show you examples of MySQL IF.
What is IF MySQL function?
The IF function returns a value if the condition is true. If the condition is false, it returns another value. The syntax for using the IF function is:
IF(expression1, expression2, expression3)
Alternatively, you may also write like this:
IF(condition, true_value, false_value)
This is how it works:
- The first expression in the IF function is the condition. For example, a<=b or name = ‘Mike’ etc.
- Second argument is the value if the condition is true.
- If the condition is false, the IF function returns expression 3.
The example of IF function in MySQL
In the first example of IF function, I used no table data. Instead, simple values are used as a condition and returned values for showing how IF function works.
The query:
SELECT IF(10>5, "True", "False") AS Result;
The output:
True
As the first expression, I used if 10 is greater than 5 then return expression 2 (True), otherwise expression 3 (False). As 10 is greater than 5 (True) so it returned the second expression.
Using table data with IF function
For this query, I am using the table data of the employees’ table. We will get the name of employees, their salary and the IF function is used to tell the level of salary as “High” or “Low” based on the salary of the employee. Have a look:
SELECT employee_name, employee_salary, IF(employee_salary>=4000,"High","Low") AS Level FROM tst_employees;
The result:
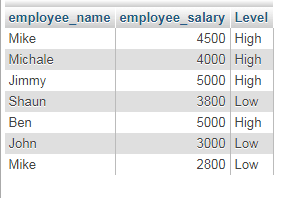
Note that, the “Level” is not the part of tst_employees table. But we created it for this result-set based on the IF function.
Using nested IF example
The following example shows using a nested IF function. Again, I used employee’s table salary column as shown below:
SELECT employee_name, employee_salary, IF(employee_salary <= 3000, 'Low', IF(employee_salary <= 4000, 'Handsome', 'High')) AS "Salary Status" FROM tst_employees;
The result-set:
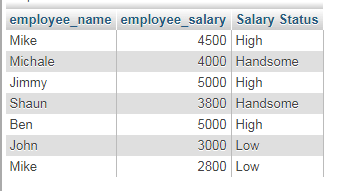
What is IF statement?
The IF statement allows executing one or more given statements if the condition is true. You may use more than one conditions by using the ELSEIF statement.
If none of the conditions are true then the ELSE part statements (if given) are executed. The general way of using the IF statement is:
IF condition THEN statement(s) [ELSEIF condition THEN statement(s)] ... [ELSE statement(s)] END IF
So, if you have a little programming background, this should look familiar and easy to understand.
The keyword IF is followed by a condition. For example:
IF a>b THEN
After the condition, THEN kewword is used and there you will provide one or more statements to execute if that condition is true.
Optionally, you may use ELSEIF for giving more conditions if the first condition fails.
If none of the condition is true then the ELSE part statements are executed.
An example of IF statement
The following MySQL function shows the simple usage of IF..THEN..ELSEIF statement. The function takes an input salary value. This is checked in the MySQL IF statement and returns the level of salary as the output.
See how IF, ELSEIF is used:
DELIMITER // CREATE FUNCTION Set_level ( emp_sal Float ) RETURNS varchar(20) BEGIN DECLARE e_sal_level VARCHAR(40); IF emp_sal <= 3500 THEN SET e_sal_level = 'Low Salary'; ELSEIF emp_sal > 3500 AND monthly_value <= 5000 THEN SET e_sal_level = 'Avg Salary'; ELSE SET e_sal_level = 'High Salary'; END IF; RETURN income_level; END; DELIMITER ;
Note: The IF statement is generally used in the functions or stored procedures.
