The Java equals() method is used to compare objects. The equals() returns true if this object is equal to the given object. Otherwise, it returns false.
Belongs to:
The equals() method belongs to the object class. As such, all classes belong to the object class, so equals() method is automatically defined for all classes.
That also means you may compare strings, integers, floats, double or any other objects as using the equals() Java method.
Syntax of using equals()
Following is the syntax of using the equals() method:
public boolean equals(Object obj)
for example, if we have x and y objects then:
x.equals(y)
- The equals() will return true if x and y are equal.
- If x is not equal to y then it returns false.
See the following section for examples of using equals method for comparing strings, integers, and other objects.
The example of comparing string using equals()
For this example, a string object is created and assigned a value. The second string object value is assigned by the user input using scanner class.
After that, the Java equals method is used to compare both strings and see the output:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
String strComp1 = "Compare by equals()";
//Taking input string for equality check
Scanner readInput = new Scanner(System.in); // Reading from System.in
System.out.println("String to Compare? ");
String strComp2 = readInput.nextLine();
Boolean x;
x = strComp1.equals(strComp2);
if (x){
System.out.println("Both Srings are the same");
}
else {
System.out.println("Strings are different!");
}
readInput.close();
}
}
As I entered different strings, the following is the result:
Result 1: String to Compare? Compare by equals() Both Strings are the same Result 2: String to Compare? Hello Java Strings are different! Result 3: String to Compare? compare by equals() Strings are different!
In the third result, the difference is ‘c’ and ‘C’ but equals() returned as false. For more on string comparison with equals and other methods visit this tutorial: compare strings in Java.
Note: The String equals() method overrides the object class equals() method.
Comparing Integer objects by Java equals() method
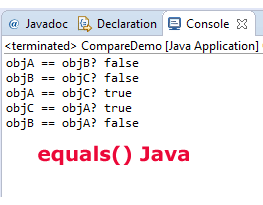
Now, let us look at the usage of equals method for equality check of Integer objects. For that, three Integer objects are created and compared by using the equals() method and the result is displayed:
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
Integer objA = 10;
Integer objB = 25;
Integer objC = 10;
System.out.println("objA == objB? " + objA.equals(objB));
System.out.println("objB == objC? " + objB.equals(objC));
System.out.println("objA == objC? " + objA.equals(objC));
System.out.println("objC == objA? " + objC.equals(objA));
System.out.println("objB == objA? " + objB.equals(objA));
}
}
The Output:
Similarly, you may check the equality of Float, Long, and Double objects. Just like the String equals(), the Integer equals() also overrides the object class equals() method.
Note: As equals() method works with objects, you may not provide primitive type int, float, double etc. variables.
Comparing a String object to Integer example
Sounds interesting? Suppose, your string contains numbers and you want to compare it with numeric objects like Integer, Floats, Double etc. Will equals() method work on that?
The answer is yes. You may compare different type objects for checking the equality. Have a look at this example:
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
Integer ObjInt = 55;
String ObjStr = "55";
System.out.println("ObjInt == objC? " + ObjInt.equals(ObjStr));
System.out.println("objC == ObjInt? " + Integer.valueOf(ObjStr).equals(ObjInt));
System.out.println("ObjInt == ObjStr? " + ObjInt.equals(Integer.valueOf(ObjStr)));
}
}
The result:
ObjInt == objC? false
objC == ObjInt? true
ObjInt == ObjStr? true
We may draw the following:
- Strings can be compared with numeric objects.
- If string’s number is equal to the numeric object like integer, the result will be false.
- If you convert a string into the number by using one of the methods like valueOf, and numbers are the same, it returns true.
The example of equals() with Float and Double objects
See the code below where two objects; one Float and the other Double are compared by using equals() method:
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
Float Objflt = 55.55f;
Double Objdbl = 55.55d;
System.out.println("Objflt == Objdbl? " + Objflt.equals(Objdbl));
}
}
The output:
Objflt == Objdbl? false
Using an object with null in equals?
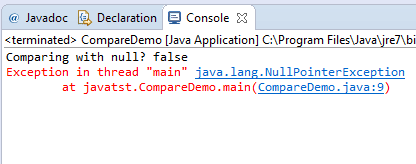
The output will simply be false if an object compared is null as using the equals() method. Otherwise, it will produce a NullPointerException error:
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
String str = null;
String str2 = "Test null";
System.out.println("Comparing with null? " + str2.equals(str));
System.out.println("Comparing with null? " + str.equals(str2));
}
}
The output: