How to Convert String to Int in Java
The string to integer or float (number) conversion is quite common while doing programming in different programming languages and so in Java.
For example, when taking the user input for numbers, the default is taken as strings.
In order to perform mathematical operations or use string numeric characters as numbers in your program, you have to convert the strings into numbers. However, that string must be the int representation that needs to be parsed.
In this tutorial, we will explain how to convert string to int in Java by using two ways:
parseInt
String numberStr = "421"; int number = Integer.parseInt(numberStr);
valueOf
String numberStr = "421"; int number = Integer.valueOf(numberStr);
Java parseInt method – First solution
Java comes up with built-in functions to let us convert strings to int. The parseInt method converts a string into the Java primitive int type. The syntax of using the parseInt method is:
- The parseInt method parses the given string as a signed decimal integer.
- All characters in the string argument must be decimal digits.
- Otherwise, the NumberFormatException exception is raised.
- The only allowed character is the minus sign (-).
The parseInt method can also be used as follows:
An example of parseInt method
The following example shows how to use the parseInt method for converting a string to an int.
public class conversion_demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int num_a =Integer.parseInt("421");
System.out.println("The int after converision:" +num_a);
}
}
Output:
You may also use the parseLong method if the string is a large number that is beyond the range of int type.
What if a string is float number?
If a Java string to be converted into numbers is a float (e.g. 123.456) then you may use parseFloat and for larger numbers parseDouble method.
See the following demo where not only numbers are converted to float but also used for multiplication with another number:
public class conversion_demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
float num_a = Float.parseFloat("587.989");
double num_b =Double.parseDouble("4217686.25");
float num_c = num_a * 2;
System.out.println("The float after converision:" +num_a +"\n");
System.out.println("The Double after converision:" +num_b +"\n");
System.out.println("Multiply result: " +num_c);
}
}
Output:
The float after converision:587.989
The Double after converision:4217686.25
Multiply result: 1175.978
What if a string contains non-numeric?
As mentioned earlier, the parseInt Java method throws an error if the given string contains non-numeric number or characters other than numbers and (-) sign. This is shown in the example below:
public class conversion_demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str_conv = "Ok 123 No";
long num_a = Long.parseLong(str_conv);
System.out.println("The int after converision:" +num_a);
}
}
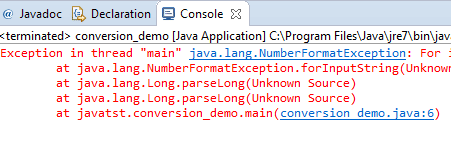
You see, even if the given string contains a number, however, it also contains other characters. So an error is thrown which is NumberFormatException.
Second solution – Using the valueOf Java method
You may also use valueOf method for converting the string into integer. The valueOf is the method of the Integer class.
This is how the valueOf method can be used with variations:
First way:
- The valueOf method returns the Integer instance that holds the given string “s” value.
- Just like the parseInt method, the string argument is interpreted as signed decimal integer.
- A NumberFormatException exception is thrown if string could not be converted to Integer. For example, the given string contains characters other than numbers with the exception of (-) sign.
- The (-) represents the negative number.
Second way:
In this case, the given primitive int is converted to integer object.
Third way:
The valueOf method returns an Integer object where the second argument is radix.
See the following examples of using the valueOf method.
The example of converting string to integer by valueOf
For this example, two Integer objects are created and assigned the string values; one with negative and other with a positive number in the string:
public class conversion_demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Integer num_x =Integer.valueOf("9");
Integer num_y =Integer.valueOf("-77");
System.out.println("The integer with string argument: " +num_x);
System.out.println("The Integer with negative string argument: " +num_y);
}
}
The output:
The Integer with negative string argument: -77
The string contains other characters than the number example
For this example, I have used the scanner class for taking the input from the user. The next() method of the scanner class takes the input as a string and it is stored in a String object.
This string object is passed to the valueOf method. Now, I “accidentally” entered a non-numeric character to convert this into an Integer. See what it outputs:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class conversion_demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); // Reading from System.in
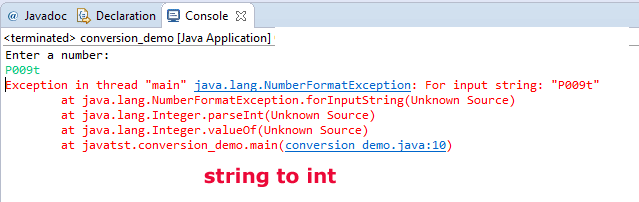
System.out.println("Enter a number: ");
String stra = reader.next();
Integer num_x =Integer.valueOf(stra);
System.out.println("The integer with string argument: " +num_x);
reader.close();
}
}
Converting string to float and double by valueOf
You may use the following syntax for returning the float and double by using the valueOf method:
Float.valueOf(str)
Double.valueOf(str)
See a demonstration below:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class conversion_demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); // Reading from System.in
System.out.println("Enter a number: ");
String stra = reader.next();
System.out.println("Enter large float number: ");
String strb = reader.next();
Float num_x = Float.valueOf(stra);
Double num_y = Double.valueOf(strb);
System.out.println("The Float: " +num_x);
System.out.println("The Double: " +num_y);
reader.close();
}
}
The output as I entered the values for float and double:
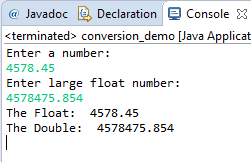
You can see, both string entries are converted to float and double, respectively.
Conclusion:
Both parseInt and valueOf methods can be used for converting int to strings in Java programs.
The parseInt method returns a primitive int type while valueOf returns Integer object.
