Change the Date Format in Excel
If you require displaying the date like this 2-Feb-2010 or August 1, 2015 etc. while entering dates you may change the settings in Excel easily.
If you are storing dates in Excel worksheets, the default format picked by Excel is the format set in the Control Panel.
So, if your control panel setting is “M/d/yyyy”, Excel will format the 2nd Feb 2022 date as follows:
If you require displaying the date like 2-Feb-2022 or August 1, 2022, etc. as entering dates you may change the settings in Excel easily.
In case you require permanently changing the date format that applies to current as well as future work in Excel, you should change this in the control panel.
For the current worksheet, you may set the date formatting in different ways as described in the following section with examples.
First Way: Change the date format by “Format Cell” option
The first way I am going to show you how to change the date format in Excel is by using the “Format Cells” option. Follow these steps:
Right click on a cell or multiple cells where you require changing the date format. For the demo, I have entered a few dates and selected all:
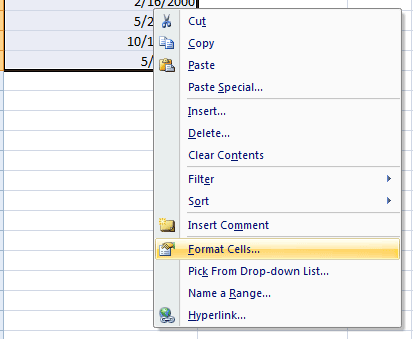
Click the “Format Cells” option that should open the Format Cells dialog.
In the Format Cells dialog, the Number tab should be pre-selected. If not, press Number tab. Under the Category, select Date. Towards the right side, you can see Type.
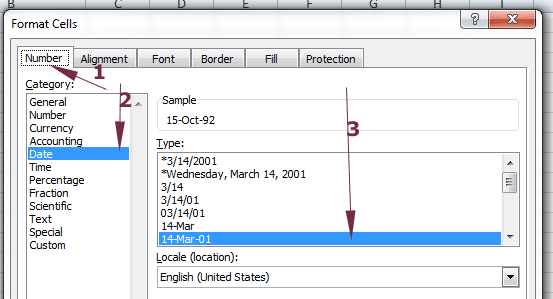
For the demo, I have selected 14-Mar-01 format and press OK. The resultant sheet after modifying date format is:
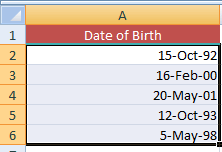
You are done!
An example of Mon-year format
The following example displays the dates in Mon-Year format e.g. Oct-92.
For that, open the "Format Cells" dialog again --> Number --> Date and select Mar-01 format.
The above sheet displays the same dates as shown below:

Similarly, you may choose any date format as per the requirement of your scenario.
Change date format by locale/location
If you wish to display the dates based on other languages then you may use the Locale (location) option in the “Format Cells” dialog.
See the following Excel sheet where I set the Arabic(UAE) option and one of its type:
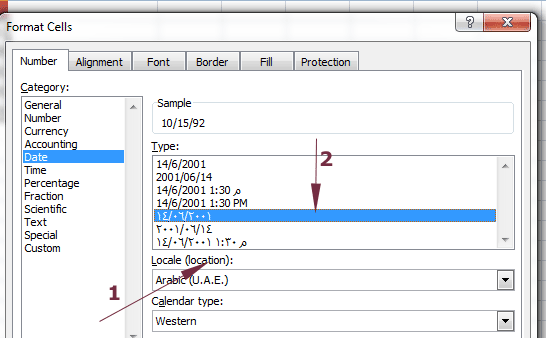
The resultant sheet for the same dates as in the above examples:
Similarly, you may choose the following locale:
- Bashkir (Russia)
- Chinese (Simplified, Singapore)
- Corsican (France)
- Danish (Denmark)
- Various options for English
- Hindi (India)
- Japanese (Japan)
- And many more
Customizing the date format
By using the date formatting codes, you may customize the dates in a flexible way. For example, displaying the short month name (Jan, Feb) by using “mmm” or the full month name by “mmmm”.
Similarly, showing the day names of the Week (Sun, Mon) by ddd or full names (Sunday, Monday) by dddd formatting code.
First, have a look at an example of customizing the date which is followed by the list of date formatting codes.
Select and right-click on the date cells that you want to customize.
Go to “Format Cells”. Under the Number --> Category, select Date and choose the closest format you wish to display e.g. “Mar 14, 2001”.
Under the Category, press Custom and towards the right side, you should see Type with various options.
Either choose a format from the available list or enter the formatting code as required in the text box under Type.
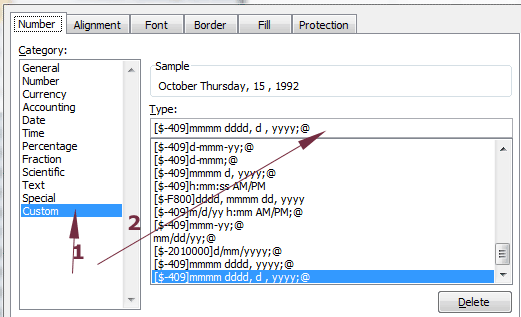
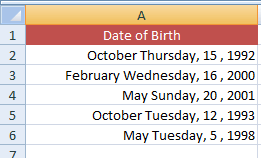
For the example, I entered the “[$-409]mmmm dddd, d , yyyy;@” and see the resultant sheet:
List of formatting codes in Excel
Following is the formatting code list that you may use to customize the dates:
Day Codes
| Format Code | Result |
|---|---|
| d | 1-31 |
| dd | 01-31 |
| ddd | Sun, Mon, Tue... |
| dddd | Sunday, Monday, Tuesday... |
Month Codes
| Format Code | Result |
|---|---|
| m | 1-12 |
| mm | 01-12 |
| mmm | Jan, Feb, Mar |
| mmmm | January, February, March |
| mmmmm | Month as the first letter of the month |
Year Codes
| Format Code | Result |
|---|---|
| yy | 00-99 |
| yyyy | 2000, 2002, 2010, etc. |
Quick way of displaying dates in default short and long formats
If you need to display dates in the short or long format with default settings, you may do it by following this:
Select the dates you wish to format in short/long date formats. For that, I chose the above example dates that were formatted in the custom format (see the last graphic):
Now, go to the Home tab, and in the Number group, click the "Number Format" box as shown below:
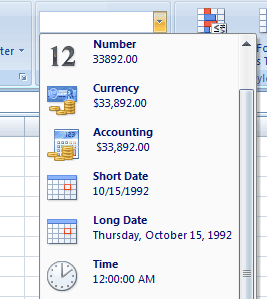
Press the "Short Date" or "Long Date" format.
Changing date format in Excel by TEXT function
The Excel TEXT function can also be used for formatting dates. The TEXT function takes two arguments as shown below:
Where the first argument can be a date cell, a number etc.
The second argument should sound familiar now; the formatting code that we just learned.
The TEXT function for formatting dates can particularly be useful if you want to keep the original date column in place and display another date set based on those dates.
An example of Full month, day, and year formatting example
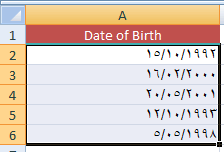
For example, the A column cells are assigned the Date of Birth dates in default format (US English) i.e. M/d/yyyy.
The corresponding B cells will display the dates in full month name, day, and year in four digits format.
The TEXT formula:
The resultant sheet with formatted dates:
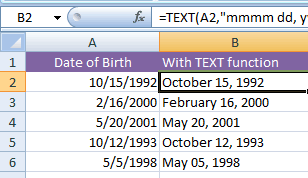
I have written the formula in the B2 cell only and copied it to B6 cell as follows.
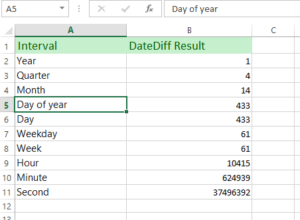
How to use the DATEDIF function in Excel
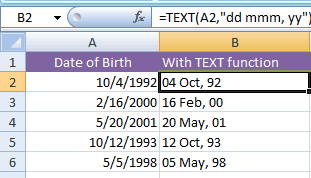
Formatting dates in d, mmm, yy by TEXT function
The following example displays the dates in the day with leading zero (01-12), short month name, and year in two-digit format.
The TEXT formula:
The resultant sheet:
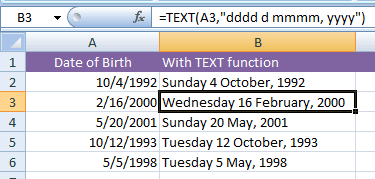
Displaying the day name as well
See the example below where the day name (Sunday, Monday, etc.) is also displayed along with the day without leading zero, full month name and year in four digits.
The formula:
The dates after formatting:
The TEXT function is more than formatting dates; this is just one usage that I explained in the above section. You may learn more about this function: The TEXT function in Excel
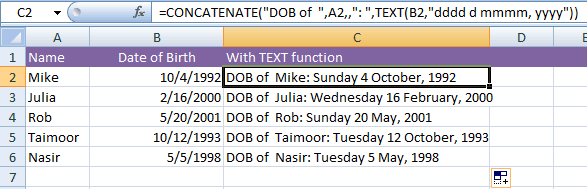
The example of concatenating formatted dates
Let us get more comfortable with date formatting and create more useful text strings as a result of joining different cells with constant literals.
In the example below, column A contains Names and column B date of birth.
In column C, I will use the CONCATENATE function where a text string is used and corresponding A and B cells are joined in the formula as follows:
This is what we get:
Formatting dates specific to language by TEXT function
As we have seen in the custom date formatting example, you can display Locale specific date style. I showed an example of displaying dates in Arabic style by using the custom date option in the “Format cells” dialog.
You may also specify the language code in the TEXT function for displaying dates based on locales.
See the following example where I displayed dates in various languages by using the TEXT function.
The resultant sheet:
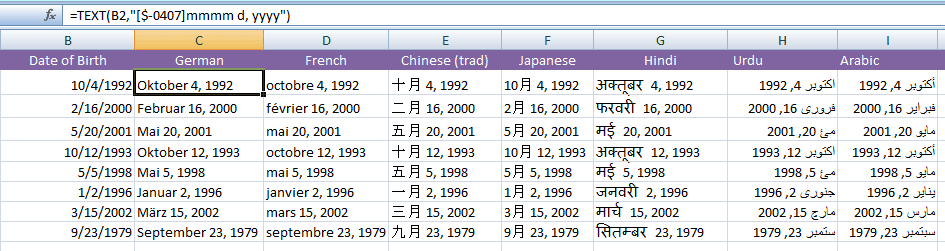
The following formulas are used for different languages:
For German:
French:
Chinese (Traditional):
Japanese:
Arabic:
For Hindi:
Urdu:
List of language codes
Following is the list of language codes that you may use in the TEXT function for locale-specific date formatting:
| Lang. Code | Language |
|---|---|
| 042B | Armenian |
| 044D | Assamese |
| 082C | Azeri (Cyrillic) |
| 042C | Azeri (Latin) |
| 042D | Basque |
| 0423 | Belarusian |
| 0445 | Bengali |
| 0402 | Bulgarian |
| 0804 | Chinese (Simplified) |
| 0404 | Chinese (Traditional) |
| 041A | Croatian |
| 0405 | Czech |
| 0406 | Danish |
| 0413 | Dutch |
| 0C09 | English (Australian) |
| 1009 | English (Canadian) |
| 0809 | English (U.K.) |
| 0409 | English (U.S.) |
| 0464 | Filipino |
| 040B | Finnish |
| 040C | French |
| 0C0C | French (Canadian) |
| 0462 | Frisian |
| 0467 | Fulfulde |
| 0456 | Galician |
| 0437 | Georgian |
| 0407 | German |
| 0C07 | German (Austrian) |
| 0807 | German (Swiss) |
| 0408 | Greek |
| 0447 | Gujarati |
| 040D | Hebrew |
| 0439 | Hindi |
| 040E | Hungarian |
| 0421 | Indonesian |
| 0410 | Italian |
| 0411 | Japanese |
| 044B | Kannada |
| 0460 | Kashmiri (Arabic) |
| 0412 | Korean |
| 0476 | Latin |
| 0426 | Latvian |
| 0427 | Lithuanian |
| 042F | Macedonian FYROM |
| 043E | Malay |
| 044C | Malayalam |
| 043A | Maltese |
| 0458 | Manipuri |
| 044E | Marathi |
| 0450 | Mongolian |
| 0461 | Nepali |
| 0414 | Norwegian Bokmal |
| 0463 | Pashto |
| 0429 | Persian |
| 0415 | Polish |
| 0416 | Portuguese (Brazil) |
| 0816 | Portuguese (Portugal) |
| 0446 | Punjabi |
| 0418 | Romanian |
| 0419 | Russian |
| 044F | Sanskrit |
| 0C1A | Serbian (Cyrillic) |
| 081A | Serbian (Latin) |
| 0459 | Sindhi |
| 045B | Sinhalese |
| 041B | Slovak |
| 0424 | Slovenian |
| 0477 | Somali |
| 0C0A | Spanish |
| 0441 | Swahili |
| 041D | Swedish |
| 045A | Syriac |
| 0428 | Tajik |
| 045F | Tamazight (Arabic) |
| 085F | Tamazight (Latin) |
| 0449 | Tamil |
| 044A | Telugu |
| 041E | Thai |
| 041F | Turkish |
| 0442 | Turkmen |
| 0422 | Ukrainian |
| 0420 | Urdu |
| 0843 | Uzbek (Cyrillic) |
| 0443 | Uzbek (Latin) |
| 042A | Vietnamese |
| 0478 | Yi |
| 046A | Yoruba |
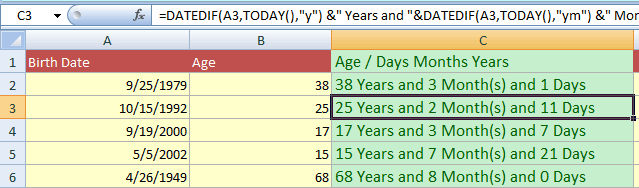
The example of calculating age in Years/Months and days
The following example uses the DATEDIF function for calculating the difference between the current date and the date of birth.
The current date is retrieved by using the TODAY() function. The Birth Date is stored in the A column. The C column displays the formatted age in years, months, and number of days.
The DATEDIF formula:
=DATEDIF(A3,TODAY(),"y") &" Years and "&DATEDIF(A3,TODAY(),"ym") &" Month(s) and " &DATEDIF(A3,TODAY(),"md") &" Days"
The resultant sheet: